监控的两要素:
- 查看系统当前(历史)的运行情况
- 系统异常时给出告警
通过两要素可使系统具备可观测性,并及时反馈系统异常。监控的目的是为了达到性能目标和维稳。
目标
监控是一种手段,目标才是目的。上监控之前要清晰的了解,系统应该达成哪些目标,稳定性应达成哪些目标。对于目标按层次分成3类:
-
业务目标
业务目标,是最高层次的目标,如PV, UV,在线用户数,乃至日营收等,其关乎产品是否有价值,是否符合团队预期。业务目标总是伴随着一些限定条件,比如时间点、投入人力、投入机器资源等。业务指标应该是项目、产品、开发负责人一起制定出来的。
-
性能目标
性能指标,服务于业务指标,如接口耗时,接口成功率,页面加载耗时等。性能指标直接关乎产品是否好用,主要应该由开发和测试制定目标,然后由开发负责。
性能指标往往会有取舍,比如延迟低但吞吐量大,入库慢但查询快,需结合场景去权衡。性能指标也要限制条件,主要是硬件资源、并发量、数据量,没有限定条件的指标是没有意义的。对于耗时,除了平均,业界往往用百分位(tp95, tp99)来观察抖动情况。
-
稳定性目标
稳定性同样服务于业务指标,性能很好,但服务长期不可用是没有意义的。系统整体的服务稳定性(SLA)、机器的负载,磁盘的剩余容量都是稳定性需要关注的。稳定性应该是开发和运维一起制定和负责的。
稳定性指标需要防患未然,如磁盘占用空间,磁盘的使用寿命,在当前时刻不会影响系统性能,但将来的某个时刻有概率会出问题,这个是需要关心的。
Prometheus
Prometheus是一种工具,可以用来监控以上三种目标。
部署
在k8s中,使用helm安装,我们用的是loki-stack, 集成了prometheus、grafana、loki:
1
|
helm upgrade --install loki --namespace=loki loki-stack --set grafana.enabled=true,prometheus.enabled=true
|
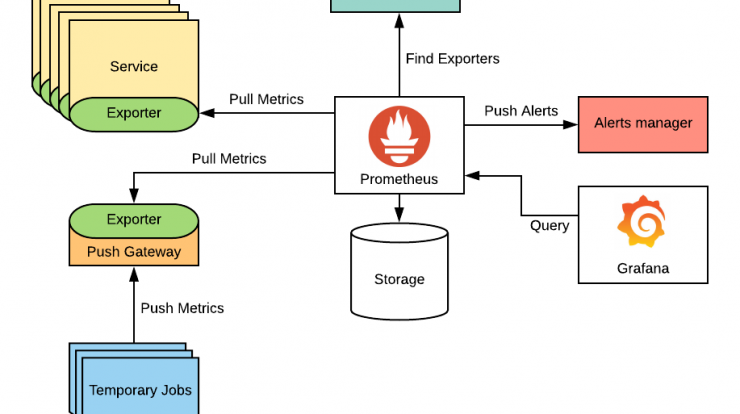
架构
metrics
prometheus的核心概念是metrics(指标)。一个metrics一般对应一项真实世界的指标,比如
1
|
http_request_total{method="POST", code=404}
|
表示http的请求数:http_request_total代表指标的名字,method和code表示指标下面有2个标签,标签可以用来做过滤。
metrics有四种类型:
- Gauge 瞬时值,前后数值没有关系,一般用来表达CPU占用率,内存占用率、网速等瞬时状态。
1
2
3
|
# HELP go_goroutines Number of goroutines that currently exist.
# TYPE go_goroutines gauge
go_goroutines 73
|
- Counter 计数器,总是递增的。一般以total后缀命名。可以结合prometheus的rate, increase函数计算QPS, 区间增量。
1
2
3
|
# TYPE http_requests_total_count counter
# HELP http_requests_total_count A counter of the total number of external HTTP requests.
http_request_total 3.7156890216e+10
|
注:counter逻辑上是递增的,但服务的重启会导致counter归零,这个会导致counter的绝对值下降,但rate等函数会处理好这种情况,所以一般无需关心。
- Summary 一般用来表示分位值。由Client SDK计算。比如计算接口耗时的TP95。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the GC invocation durations.
# TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0"} 3.291e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.25"} 4.3849e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.5"} 6.2452e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.75"} 9.8154e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="1"} 0.011689149
go_gc_duration_seconds_sum 3.451780079
go_gc_duration_seconds_count 13118
|
- Histogram 和summary类似,可以表示百分位。但由Prometheus Server端计算,CLient端只做分桶计数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
# HELP http_request_duration_seconds request duration histogram
# TYPE http_request_duration_seconds histogram
http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.5"} 0
http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="1"} 1
http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="2"} 2
http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="3"} 3
http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="5"} 3
http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="+Inf"} 3
http_request_duration_seconds_sum 6
http_request_duration_seconds_count 3
|
exporter
exporter会暴露一个Http的接口,供Prometheus来采集Metrics。可以:
- 业务服务集成Prometheus Sdk, 直接收集和暴露Metrics接口。适合我们自己编写的服务。golang建议使用go-metrics这个sdk
- 编写独立的服务,专门用来收集指标和暴露Metrics接口。适合对第三方服务开发exporter。业界也有大量的exporter供我们使用:mysql-exporter,node-exporter等。
在exporter的deployment中配置pull的开关和端口, 配置完成后prometheus server会定时来拉取metrics。
1
2
3
|
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
prometheus.io/port: '9090'
|
除了exporter,还可以通过将metrics委托给push-gataway来收集,push-gateway自身是一个exporter,适用于启动时间端的服务(比如job)。
如果exporter不属于k8s的pod, 需要配置prometheus的scrape_configs,具体可以参考这里。
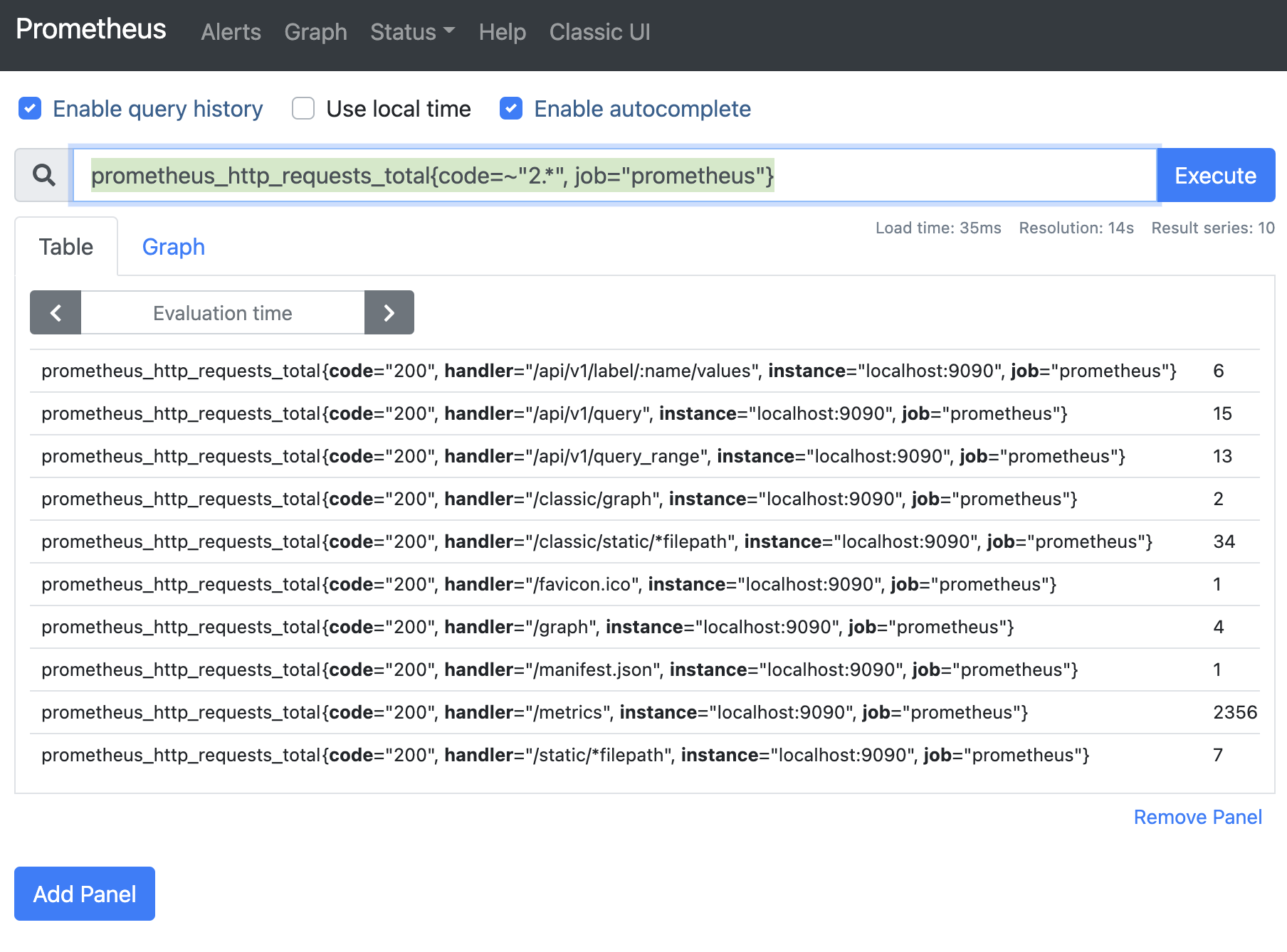
promql
可以在prometheus的web页面进行简单的metrics查询。
samples
1
2
3
4
5
|
http_requests_total # 查询http_requests_total的数据
http_requests_total{job="prometheus"} # 过滤job=prometheus
http_requests_total{job="prometheus"}[5m] # 查询最近5分钟,job=prometheus的数据
rate(http_requests_total{job="prometheus"}[5m]) # 查询最近5分钟,job=prometheus的QPS数据
increase(http_requests_total{job="prometheus"}[5m]) # 查询最近5分钟,job=prometheus的增量值
|
Grafana
grafana是最终展示prometheus metrics报表的地方。简单来说分2步:
- 添加prometheus数据源
- 配置dashboard 配置dashboard的过程即是编写promql的过程。
dashboard库中可以找到一些现成的dashboard。
dashboard的导入导出
我们grafana的dashboard一般是在公司的开发环境配置好的,但生产环境是在客户的私有网络,如何同步? 官方只支持单个dashboard都导入和导出。最后我们采用dump&import db文件(sqlite)的方案。
- 拷贝开发环境的grafana db文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#!/bin/bash
export KUBECONFIG=/home/dev/k8s.conf
pod=$(kubectl get pod -n loki | grep loki-grafana | awk '{print $1}')
echo "grafana pod=$pod"
rm -f ./grafana.db
kubectl -n loki cp "$pod:/var/lib/grafana/grafana.db" ./grafana.db
|
- 过滤开发环境的用户数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect("./grafana.db")
file = open("./grafana.sql", "w")
blacklists = ["annotation", "alert_notification"]
blacklists = ["INSERT INTO \"{}\"".format(bl) for bl in blacklists]
print("blacklists: ", blacklists)
create_cmds = ["CREATE INDEX", "CREATE UNIQUE INDEX", "CREATE TABLE"]
insert_cmd = "INSERT INTO"
lines = []
for line in conn.iterdump():
blacklist = False
for bl in blacklists:
if line.startswith(bl):
blacklist = True
break
else:
pass
if not blacklist:
for create_cmd in create_cmds:
if line.startswith(create_cmd):
line = line.replace(create_cmd, create_cmd + " IF NOT EXISTS ")
break
if line.startswith(insert_cmd):
line = line.replace(insert_cmd, "INSERT OR REPLACE INTO")
lines.append(line)
if len(lines) < 10:
print("error sql lines")
file.writelines(lines)
|
- 导入现场
Alerts
这里其实有两个Alert, 一个是Prometheus的Alert,一个是Grafana的Alert。我们这里采用的是Prometheus的Alert,其更灵活和强大。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
# 示例1
- alert: KubeControllerManagerDown
annotations:
message: KubeControllerManager has disappeared from Prometheus target discovery.
expr: |
absent(up{job="kube-controller-manager"} == 1)
for: 15m
labels:
severity: critical
# 示例2
- alert: KubePodNotReady
annotations:
message: Pod {{ $labels.namespace }}/{{ $labels.pod }} has been in a non-ready
state for longer than an hour.
expr: |
sum by (namespace, pod) (kube_pod_status_phase{app_kubernetes_io_name="kube-state-metrics", phase=~"Pending|Unknown"}) > 0
for: 1h
labels:
severity: critical
|
上面是2个alert规则的示例:
- alert名字:KubeControllerManagerDown
- annotations:alert自定义的数据,这里面我们添加了一个message, 表示alert的文本描述。
- expr: 触发alert点表达式。由promql语句组成,会有一个比较条件,最终表达式返回的是bool类型。
- for: 持续的时间,大于则触发alert
- labels: 标签数据,和annotations的区别是labels会基于metrics自动填充,alert配置时可以覆盖值。
pormetheus执行alert rule的检测,一旦有新的alert, 则会推送给alertmanager, alertmanager可以:
- web页面可以查看alert, 临时屏蔽alert的推送
- 配置webhook, 将alert发给下游,比如钉钉
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
receivers:
- name: webhook_all
webhook_configs:
- url: http://10.1.0.200:8060/dingtalk/webhook_default/send
send_resolved: false
- name: mention_dev1
webhook_configs:
- url: http://10.0.0.200:8060/dingtalk/mention_dev1/send
send_resolved: false
|
- 配置route, 将不同的alert推送给不同的receiver, 实现alert@到人的效果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
route:
group_wait: 30s
group_interval: 5m
receiver: webhook_all
- match_re:
alertname: .*空间不足
receiver: mention_dev1 # 如果是空间不足相关的报警,则通知dev1
|
钉钉
prometheus-webhook-dingtalk可以适配alertmanager, 将alert推送给钉钉。
参考:
- Prometheus的方法
- Promeetheus的counter是如何工作的
- GRAFANA SUPPORT FOR PROMETHEUS

